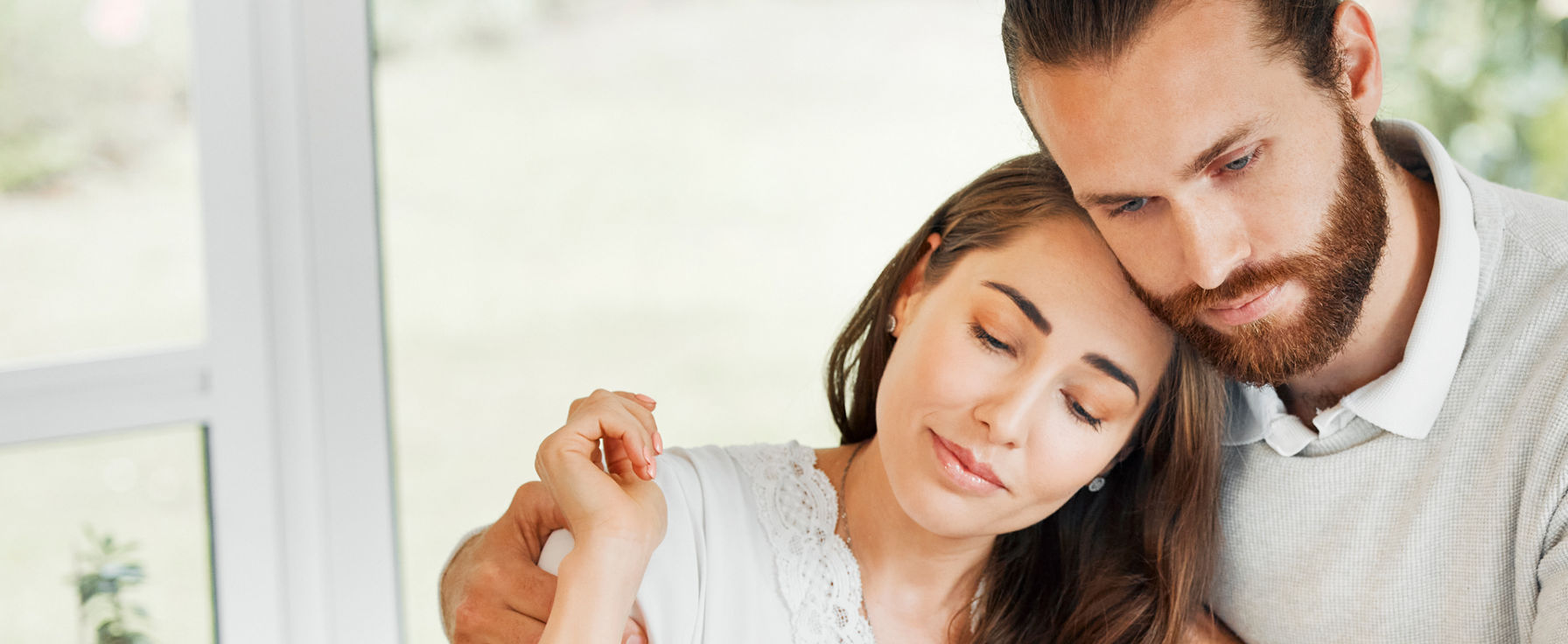
Trichomonas vaginalis (T. vaginalis) is a protozoan pathogen that causes trichomoniasis, a common, curable sexually transmitted infection.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there are about 2.6 million trichomoniasis infections in the United States. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates there were more than 156 million cases worldwide in 2020. About 70 percent of individuals infected with T. vaginalis do not experience symptoms.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in women can include:
- Vaginal discharge
- Pain, itching, burning of genitals
- Dysuria
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in men can include:
- Irritation or itching in the penis
- Dysuria
- Urethral discharge
Symptoms fluctuate in intensity and may persist for weeks or months. For women, symptoms usually worsen during menses and pregnancy. Left untreated, trichomoniasis may increase the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight as well as lead to infertility in women.