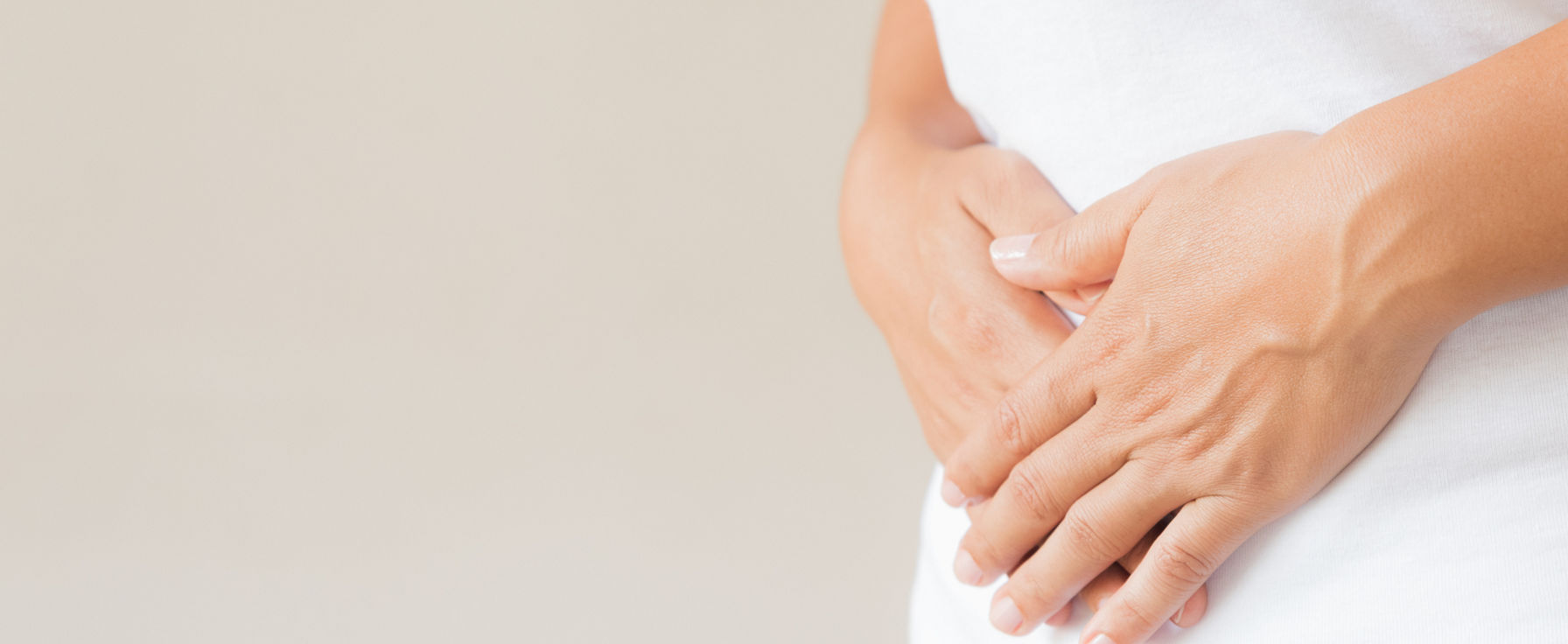
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation in the mucosa of the large intestine (colon and rectum), leading to the development of ulcers. While the cause of ulcerative colitis is not definitively known, medical professionals believe that possible causes include:
Genetics
Autoimmune disease
Gut microbiome changes
Virus or bacteria triggers
Anyone can develop ulcerative colitis, however, individuals at higher risk include those:
Between 15 and 30 years old
Living in the United States or Northern Europe
With a family history of inflammatory bowel disease
Of Jewish descent
As a lifelong disease, people with ulcerative colitis can experience extended periods of time with symptoms, as well as periods of time without symptoms. Most people have mild to moderate symptoms that can include:
Diarrhea
Abdominal cramping and pain
Rectal pain
Blood or puss in the stool
Constipation
Anemia
Weight loss
Fatigue
Most individuals with ulcerative colitis will have a full life expectancy. For severe ulcerative colitis cases, complications can arise including:
Severe bleeding
Perforated colon
Severe dehydration
Toxic megacolon
Blood clots
Osteoporosis
Skin, joint and eye inflammation
The development of ulcerative colitis cannot be prevented. However, individuals with the condition can take measures to alleviate flare-ups and manage symptoms. Taking medications that are intended to curb inflammation in the large intestine can help keep ulcerative colitis in remission. Understanding certain lifestyle factors that may trigger flare-ups will assist individuals better manage their conditions. Some ways to manage flare-ups include:
Reducing stress
Physical exercise
Avoiding certain medications (e.g., non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, some antibiotics)
Avoiding trigger foods (e.g., those of fried, high fiber, high sugar, and/or of alcohol nature)
There is an increased risk of colon cancer for people with ulcerative colitis, so regular testing is important.
There are several tests which may be used to diagnose ulcerative colitis and complications of the disease. Testing is also used to rule out other diseases with similar symptoms. Types of tests include:
Blood tests – to detect infection, inflammation and anemia
Stool tests – to screen for white blood cells and certain proteins indicating infection or inflammation
Colonoscopy – to view the colon and/or take tissue biopsies
Sigmoidoscopy – to view the rectum
CT scan – to reveal inflammation of the colon
Treatment for ulcerative colitis usually includes medication and/or surgery. Medicines to reduce inflammation of the large intestine and to calm the immune system are prescribed depending on the individual’s condition and severity of disease. Common medications may include:
Aminosalicylates (e.g., sulfasalazine, mesalamine, balsalazide, olsalazine)
Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone, budesonide)
Immunomodulators (e.g., 6-mercaptopurine, azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate)
Biologics (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, vedolizumab, ustekinumab)
Small molecule medications (e.g., tofacitinib, upadacitinib, ozanimod)
Seventy percent of people respond well to medication. For those who do not tolerate medication well, do not experience relief from symptoms, or experience complications as result of medication, surgery is an option as the next level of treatment intervention. A proctocolectomy removes the colon and rectum, eliminating ulcerative colitis.
A procedure called a J-pouch (ileoanal anastomosis) involves forming a pouch from the small intestine and attaching it to the anus. This allows the patient to eliminate waste naturally. This procedure could involve two or more successive surgeries to complete.
If the J-pouch methodology is not an option, the surgeon may create an opening in the abdomen and attach an ostomy bag that will collect waste. The ostomy bag will be worn at all times and be changed several times a day.
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10351-ulcerative-colitis
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ulcerative-colitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353326
- https://www.webmd.com/ibd-crohns-disease/ulcerative-colitis/causes-ulcerative-colitis
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/ulcerative-colitis