ln the past, the potential for bilirubin to cause brain damage – kernicterus – in infants was assessed by calculating indirect bilirubin (IBIL).
Routinely used diazo methods exhibit considerable variation due to reaction time, reaction mixture pH or endogenous interferents.
Incorrect IBIL results increase the probability of unnecessary treatments. Using a more accurate method of measuring unconjugated bilirubin allows to apply therapeutic interventions with greater certainty.
The solution
The Vitros BuBc Slide provides true measurement of both conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin fractions. It shows greater specificity and increased robustness against interferences than traditional wet chemistry diazo bilirubin assays. This gives you precise, accurate results that add up to quality patient care.
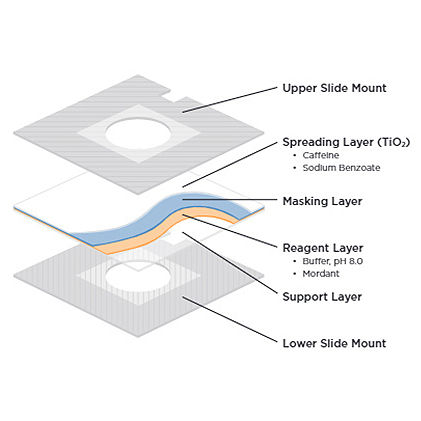
Spreading layer
- Traps large molecules like delta bilirubin delta bilirubin – DELB – (Bc bound to albumin) which is not measured.
Masking layer
- Optically blocks potentially interfering compounds trapped in the spreading layer, such as hemoglobin, preventing them from interfering with the measurement.
References
1. Chan KM, Scott MG, Wu TW, et al. Inaccurate values for direct bilirubin with some commonly used direct bilirubin procedures. Clin Chem. 1985;31(9):1560-1563.






